midiogre.augmentations package
Submodules
midiogre.augmentations.duration_shift module
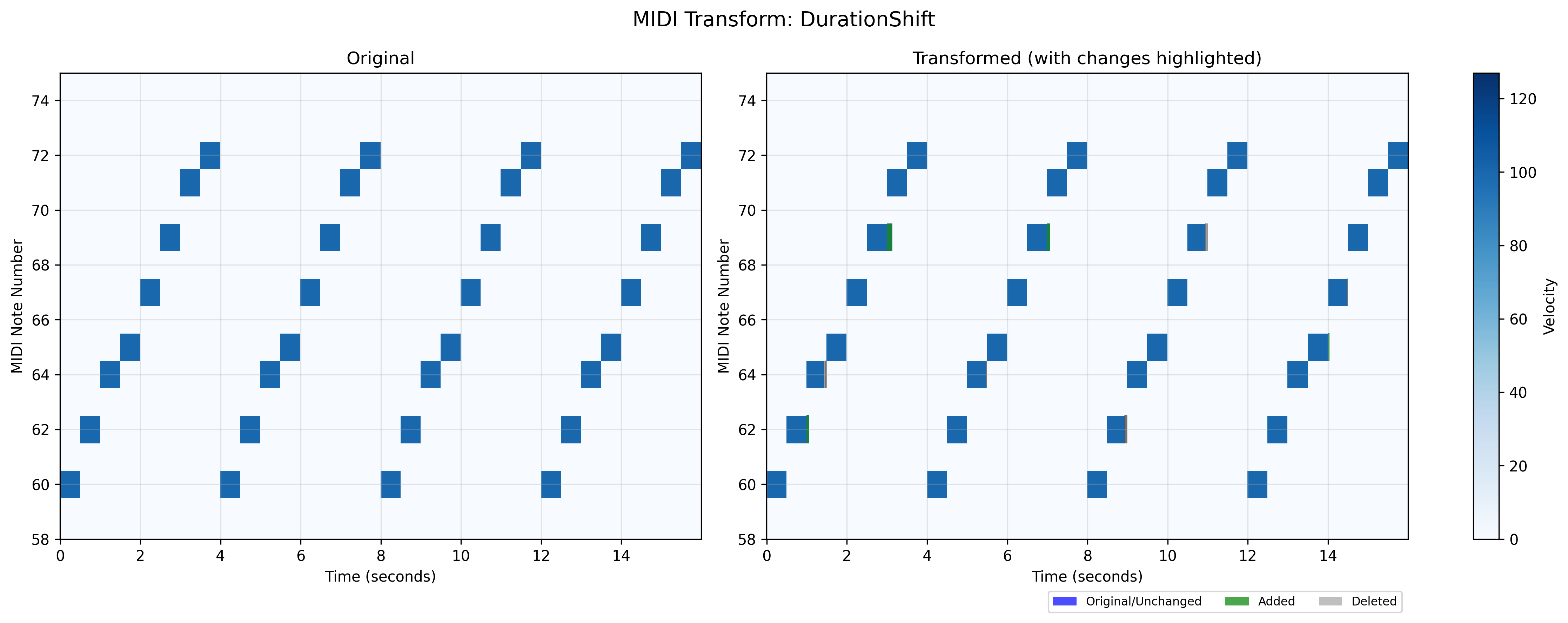
MIDI note duration augmentation module.
This module provides functionality to randomly modify the durations of MIDI notes while preserving their onset times. The durations can be extended or shortened, allowing for articulation variations while maintaining rhythmic timing.
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import DurationShift
>>> import pretty_midi
>>>
>>> # Create transform that modifies note durations by up to 0.5 seconds
>>> transform = DurationShift(
... max_shift=0.5,
... mode='both',
... p=0.5
... )
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI('song.mid')
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- class midiogre.augmentations.duration_shift.DurationShift(max_shift, mode='both', min_duration=1e-06, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly modifying MIDI note durations.
This transform allows for random modification of note durations while preserving their onset times. Each selected note can be shortened or lengthened by a random amount within the specified range. The shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for varied articulation.
The duration shift is applied with probability p to each selected instrument, and within each instrument, to a random subset of notes determined by p. All shifts are automatically clipped to ensure notes maintain a minimum duration and don’t extend beyond the track end.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds by which a note duration can be modified. Must be positive.
mode (str) – Type of duration modification. One of: - ‘shrink’: Only shorten notes - ‘extend’: Only lengthen notes - ‘both’: Allow both shortening and lengthening Default: ‘both’
min_duration (float) – Minimum allowed note duration in seconds. Notes will not be shortened below this value. Default: 1e-6
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the probability of modifying each note. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - max_shift is not positive - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘shrink’, ‘extend’ - min_duration is not positive - p_instruments is not in range [0, 1] - p is not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that only extends notes by 0.1-0.3 seconds >>> transform = DurationShift( ... max_shift=0.3, ... mode='extend', ... min_duration=0.1, ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.4 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', min_duration=1e-06, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the DurationShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds for duration modifications.
mode (str, optional) – Type of duration modification (‘shrink’, ‘extend’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
min_duration (float, optional) – Minimum allowed note duration in seconds. Default: 1e-6
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Probability of modifying each note. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the duration shift transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Randomly selects a subset of notes based on p 2. Generates random duration shifts based on mode and max_shift 3. Applies the shifts while maintaining onset times and ensuring valid durations
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with modified note durations.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The transform maintains the onset time of all notes
Notes are modified independently, allowing for varied articulation
- Duration changes are clipped to ensure:
Notes maintain the minimum duration
Notes don’t extend beyond the end of the track
midiogre.augmentations.note_add module
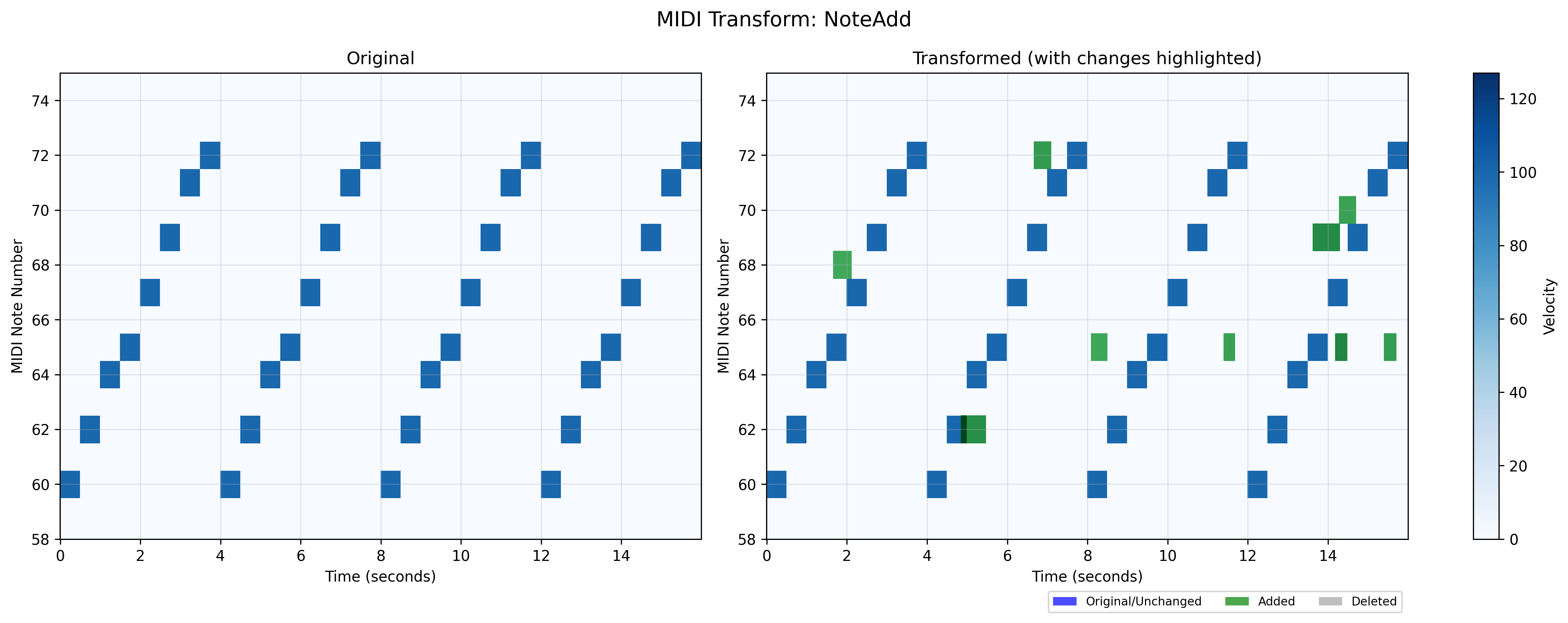
MIDI note addition augmentation module.
This module provides functionality to randomly add new notes to MIDI tracks. The added notes can be configured in terms of their pitch range, velocity range, and duration range, allowing for controlled density variations in the music.
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import NoteAdd
>>> import pretty_midi
>>>
>>> # Create transform that adds notes in the middle register
>>> transform = NoteAdd(
... note_num_range=(48, 72), # C3 to C5
... note_velocity_range=(60, 100),
... note_duration_range=(0.2, 0.8),
... p=0.3
... )
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI('song.mid')
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- class midiogre.augmentations.note_add.NoteAdd(note_num_range, note_velocity_range, note_duration_range, restrict_to_instrument_time=True, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly adding new MIDI notes.
This transform allows for random addition of new notes to MIDI tracks. Each new note’s properties (pitch, velocity, duration, timing) are randomly generated within specified ranges. The number of notes added is proportional to the existing number of notes in each track.
The note addition is applied with probability p to each selected instrument. For each selected instrument, the number of notes to add is randomly chosen between 0 and p * (current number of notes).
- Parameters:
note_num_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI note numbers for new notes as (min_note, max_note). Each value must be in range [0, 127]. Example: (60, 72) for notes between middle C and C5.
note_velocity_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI velocities for new notes as (min_velocity, max_velocity). Each value must be in range [0, 127]. Example: (64, 100) for medium to loud notes.
note_duration_range (tuple[float, float]) – Range of note durations in seconds as (min_duration, max_duration). Values must be positive. Example: (0.1, 0.5) for short to medium notes.
restrict_to_instrument_time (bool) – If True, new notes will not extend beyond the end time of existing notes in the instrument. Default: True
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the maximum ratio of new notes to add relative to existing notes. Must be in range [0, 1]. Example: If p=0.2 and an instrument has 100 notes, up to 20 new notes may be added. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - note_num_range values not in [0, 127] - note_velocity_range values not in [0, 127] - note_duration_range values not positive - ranges not specified as (min, max) with max > min - p_instruments not in range [0, 1] - p not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that adds short, quiet notes in the high register >>> transform = NoteAdd( ... note_num_range=(72, 96), # C5 to C7 ... note_velocity_range=(20, 40), # Soft notes ... note_duration_range=(0.05, 0.2), # Short notes ... restrict_to_instrument_time=True, ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.15 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(note_num_range, note_velocity_range, note_duration_range, restrict_to_instrument_time=True, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the NoteAdd transform.
- Parameters:
note_num_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI note numbers for new notes.
note_velocity_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI velocities for new notes.
note_duration_range (tuple[float, float]) – Range of note durations in seconds.
restrict_to_instrument_time (bool, optional) – Whether to limit note end times. Default: True
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Maximum ratio of new notes to add. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the note addition transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Determines the number of notes to add based on p 2. Generates random notes within the configured ranges 3. Adds the new notes to the instrument track
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with added notes.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The number of notes added is random but proportional to existing notes
New notes have random properties within the configured ranges
If restrict_to_instrument_time is True, new notes won’t extend beyond the end of existing notes in the track
midiogre.augmentations.note_delete module
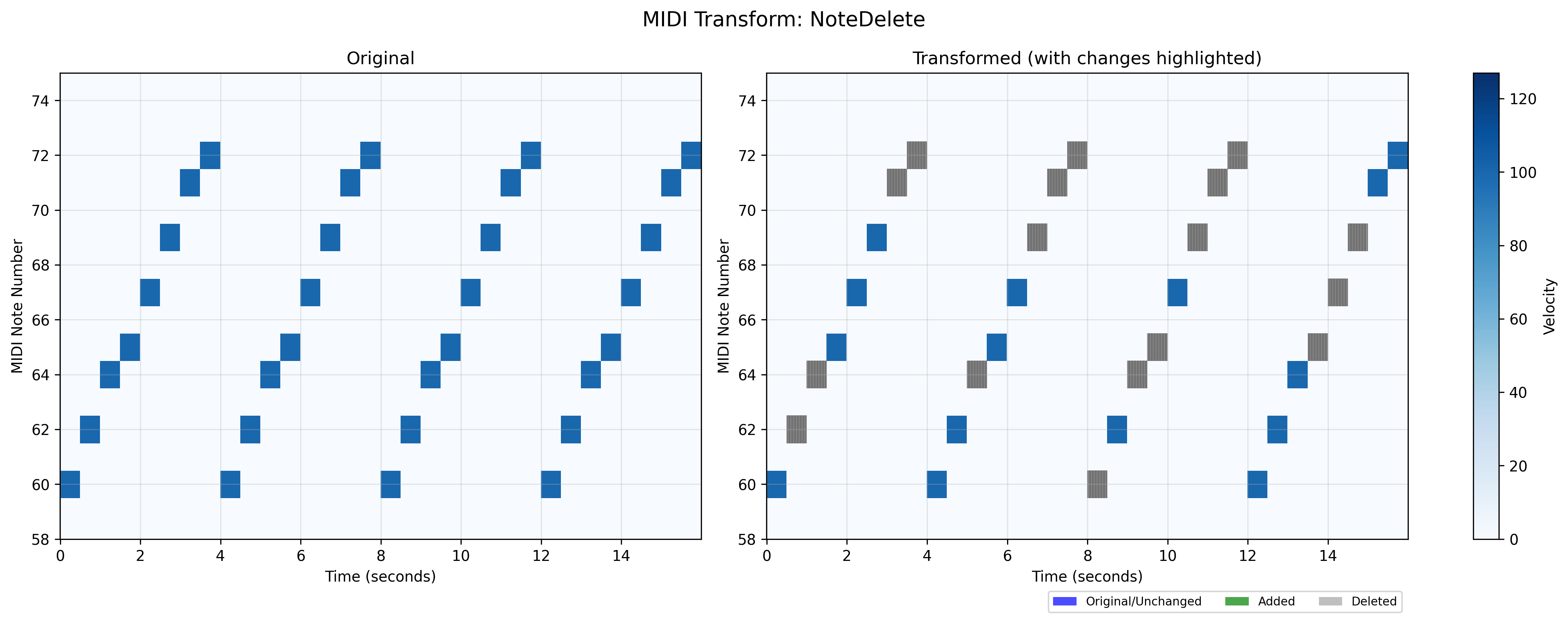
MIDI note deletion augmentation module.
This module provides functionality to randomly remove notes from MIDI tracks. The deletion process can be configured to affect a certain percentage of notes across selected instruments, allowing for controlled sparsification of the music.
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import NoteDelete
>>> import pretty_midi
>>>
>>> # Create transform that randomly removes up to 20% of notes
>>> transform = NoteDelete(p=0.2)
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI('song.mid')
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- class midiogre.augmentations.note_delete.NoteDelete(p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly deleting MIDI notes.
This transform allows for random deletion of existing notes from MIDI tracks. The deletion is applied with probability p to each selected instrument. For each selected instrument, the number of notes to delete is randomly chosen between 0 and p * (current number of notes).
- Parameters:
p_instruments (float, optional) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float, optional) – For each selected instrument, this determines the maximum ratio of notes that may be deleted. Must be in range [0, 1]. Example: If p=0.2 and an instrument has 100 notes, up to 20 notes may be deleted. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - p_instruments not in range [0, 1] - p not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that aggressively thins out notes >>> transform = NoteDelete( ... p_instruments=0.8, # Apply to 80% of instruments ... p=0.4, # Delete up to 40% of notes ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the NoteDelete transform.
- Parameters:
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Maximum ratio of notes that may be deleted. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the note deletion transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Determines the number of notes to delete based on p 2. Randomly selects notes for deletion 3. Removes the selected notes from the instrument track
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with notes deleted.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The number of notes deleted is random but proportional to existing notes
Notes are selected for deletion uniformly at random
Empty instruments (no notes) are skipped
midiogre.augmentations.onset_time_shift module
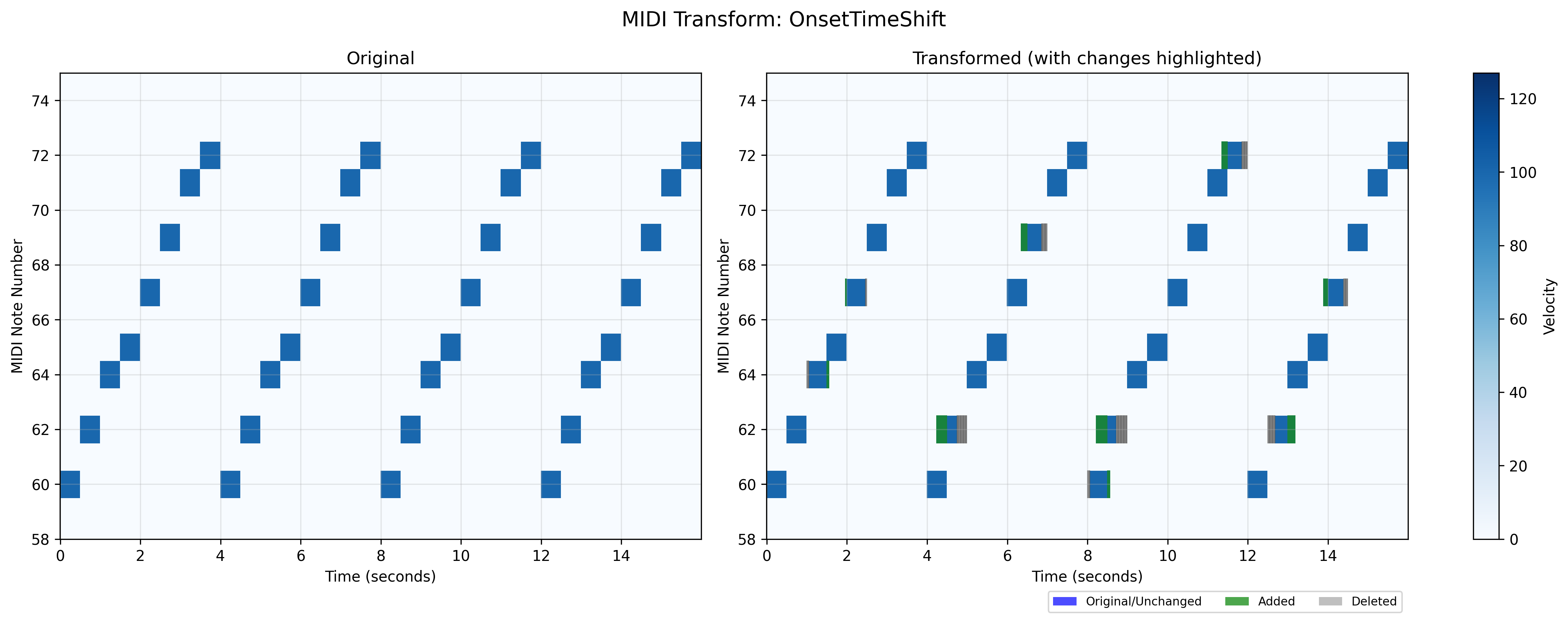
MIDI onset time augmentation module.
This module provides functionality to randomly shift the onset times of MIDI notes while preserving their durations. The shifts can be applied to move notes earlier or later in time, allowing for rhythmic variations while maintaining note lengths.
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import OnsetTimeShift
>>> import pretty_midi
>>>
>>> # Create transform that shifts note timings by up to 0.1 seconds
>>> transform = OnsetTimeShift(
... max_shift=0.1,
... mode='both',
... p=0.5
... )
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI('song.mid')
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- class midiogre.augmentations.onset_time_shift.OnsetTimeShift(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly shifting MIDI note onset times.
This transform allows for random modification of note start times while preserving their durations. Each selected note can be shifted earlier or later in time by a random amount within the specified range. The shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for complex rhythmic variations.
The onset shift is applied with probability p to each selected instrument, and within each instrument, to a random subset of notes determined by p. All shifts are automatically clipped to ensure notes stay within valid time ranges (no negative start times, no extending beyond track end).
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds by which a note onset can be shifted. Must be positive.
mode (str) – Direction of time shift. One of: - ‘left’: Only shift notes earlier (ie, advance) in time - ‘right’: Only shift notes later (ie, delay) in time - ‘both’: Allow both earlier and later shifts Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the probability of shifting each note. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - max_shift is not positive - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘left’, ‘right’ - p_instruments is not in range [0, 1] - p is not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that only delays notes by 0.05-0.15 seconds >>> transform = OnsetTimeShift( ... max_shift=0.15, ... mode='right', ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.3 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the OnsetTimeShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds for onset shifts.
mode (str, optional) – Direction of time shift (‘left’, ‘right’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Probability of shifting each note. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the onset time shift transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Randomly selects a subset of notes based on p 2. Generates random time shifts based on mode and max_shift 3. Applies the shifts while maintaining note durations and ensuring valid times
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with shifted note timings.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The transform maintains the duration of all notes
Notes are shifted independently, allowing for complex rhythmic variations
- Shifts are clipped to ensure notes stay within valid time ranges:
No negative start times
No extending beyond the end of the track
midiogre.augmentations.pitch_shift module
MIDI pitch augmentation module.
This module provides functionality to randomly transpose MIDI notes up or down while preserving their timing and velocity. The pitch shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for complex harmonic variations.
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import PitchShift
>>> import pretty_midi
>>>
>>> # Create transform that shifts pitches up or down by up to 2 semitones
>>> transform = PitchShift(
... max_shift=2,
... mode='both',
... p=0.5
... )
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI('song.mid')
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- class midiogre.augmentations.pitch_shift.PitchShift(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly transposing MIDI note pitches.
This transform allows for random transposition of MIDI notes while preserving their timing and velocity. Each selected note can be shifted up or down by a random amount within the specified range. The shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for complex harmonic variations.
The pitch shift is applied with probability p to each selected instrument, and within each instrument, to a random subset of notes determined by p. All shifts are automatically clipped to stay within the valid MIDI note range [0, 127].
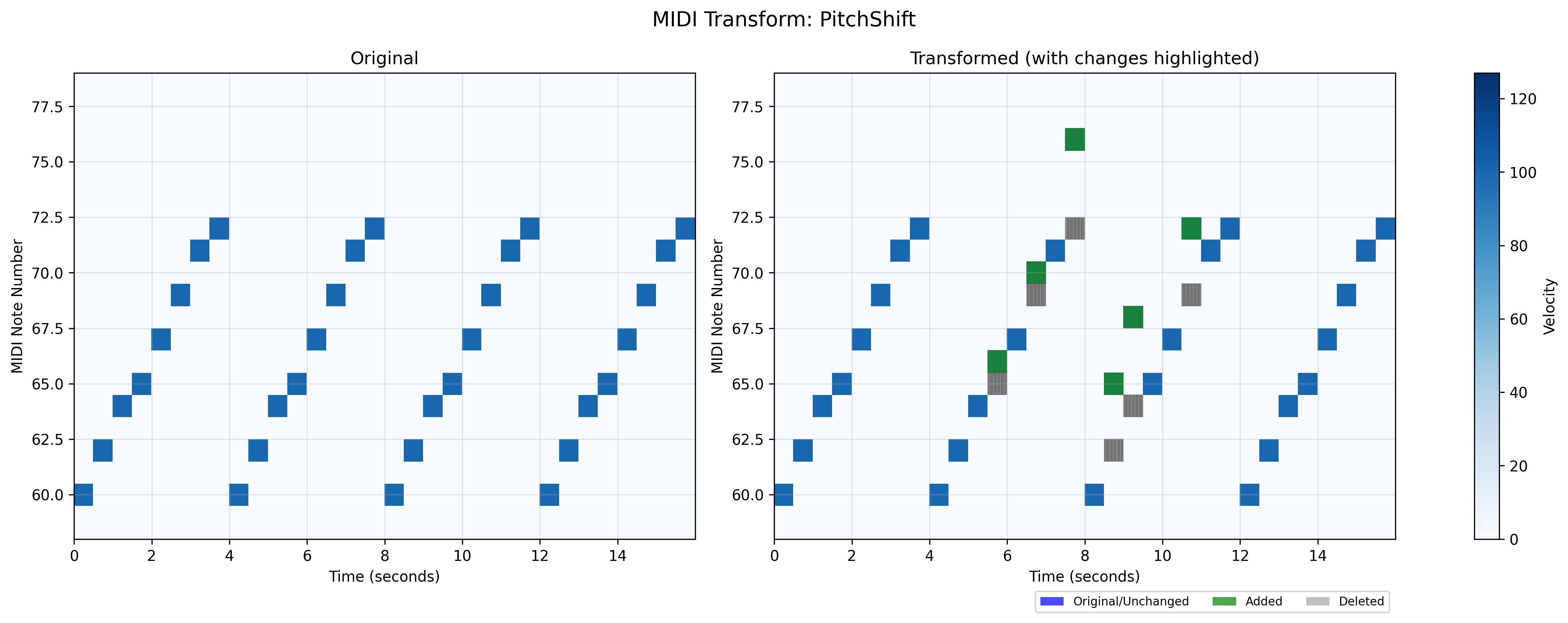
- Parameters:
max_shift (int) – Maximum number of semitones by which a note pitch can be shifted. Must be in range [0, 127].
mode (str) – Direction of pitch shift. One of: - ‘up’: Only shift pitches up - ‘down’: Only shift pitches down - ‘both’: Allow both up and down shifts Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the probability of shifting each note. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - max_shift is not in range [0, 127] - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘up’, ‘down’ - p_instruments is not in range [0, 1] - p is not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that only shifts pitches up by 1-3 semitones >>> transform = PitchShift( ... max_shift=3, ... mode='up', ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.5 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the PitchShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (int) – Maximum number of semitones for pitch shifts.
mode (str, optional) – Direction of pitch shift (‘up’, ‘down’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Probability of shifting each note. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the pitch shift transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Randomly selects a subset of notes based on p 2. Generates random pitch shifts based on mode and max_shift 3. Applies the shifts while clipping to valid MIDI note range [0, 127]
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with shifted pitches.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The transform maintains the original timing and velocity of all notes
Notes are shifted independently, allowing for complex harmonic variations
midiogre.augmentations.tempo_shift module
MIDI tempo augmentation module.
This module provides functionality to modify the tempo of MIDI files while preserving the relative timing of notes. The tempo can be shifted up or down within specified bounds, and the transform can either respect existing tempo changes or apply a single global tempo.
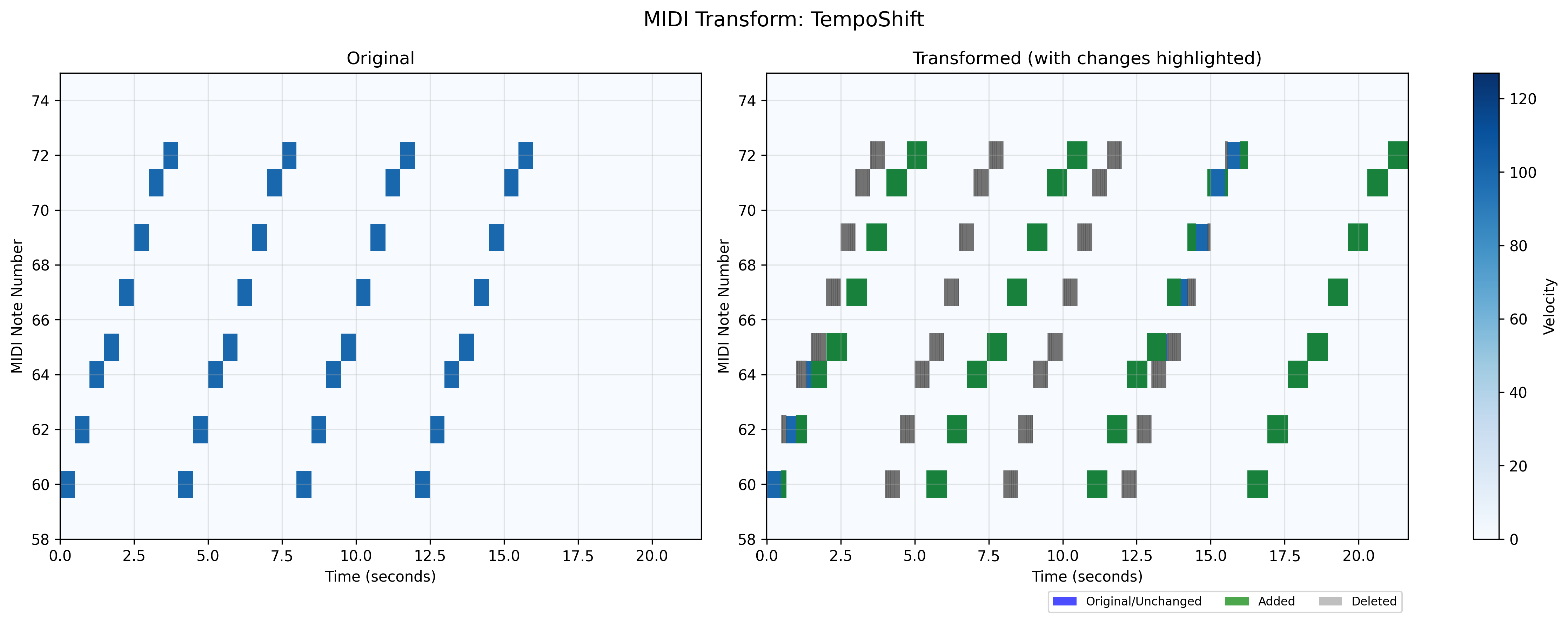
Note
This transform operates on Mido MidiFile objects. If you have a PrettyMIDI object, you must first convert it using MIDIOgre’s converters: >>> from midiogre.core.conversions import ConvertToMido >>> midi_data = ConvertToMido()(pretty_midi_obj)
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import TempoShift
>>> from midiogre.core.conversions import ConvertToMido, ConvertToPrettyMIDI
>>>
>>> # Create transform that can increase or decrease tempo by up to 20 BPM
>>> transform = TempoShift(
... max_shift=20.0,
... mode='both',
... tempo_range=(60.0, 180.0),
... p=0.8
... )
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = ConvertToMido()('song.mid') # Convert to Mido format
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data) # Apply transform
>>> pretty_midi_obj = ConvertToPrettyMIDI()(transformed) # Convert back if needed
- class midiogre.augmentations.tempo_shift.TempoShift(max_shift, mode='both', tempo_range=(30.0, 200.0), p=0.2, respect_tempo_shifts=True, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly modifying MIDI tempo.
This transform allows for random modification of MIDI tempo while preserving the relative timing of notes. It can either respect all existing tempo changes in the file or replace them with a single global tempo.
Note
This transform operates on Mido MidiFile objects. If you have a PrettyMIDI object, you must first convert it using MIDIOgre’s converters: >>> from midiogre.core.conversions import ConvertToMido >>> midi_data = ConvertToMido()(pretty_midi_obj)
The tempo shift is applied with probability p, and when applied, generates random shifts based on the specified mode and maximum shift value. The final tempo is always clipped to stay within the specified tempo range.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum value by which tempo can be randomly shifted (in BPM). Must be positive.
mode (str) – Direction of tempo shift. One of: - ‘up’: Only increase tempo - ‘down’: Only decrease tempo - ‘both’: Allow both increase and decrease Default: ‘both’
tempo_range (tuple[float, float]) – Allowed tempo range in BPM as (min_tempo, max_tempo). The transformed tempo will be clipped to stay within this range. Default: (30.0, 200.0)
p (float) – Probability of applying the tempo shift. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
respect_tempo_shifts (bool) – If True, preserves all tempo change events, shifting each while maintaining their timing. If False, replaces all tempo events with a single tempo at the start. Default: True
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘up’, ‘down’ - max_shift is not positive - tempo_range is not a tuple/list of length 2 - min_tempo is negative - min_tempo >= max_tempo
Example
>>> from midiogre.core.conversions import ConvertToMido, ConvertToPrettyMIDI >>> # Create transform that increases tempo by 10-30 BPM >>> transform = TempoShift( ... max_shift=30.0, ... mode='up', ... tempo_range=(60.0, 240.0), ... p=1.0 ... ) >>> midi_data = ConvertToMido()('song.mid') # Convert to Mido format >>> transformed = transform(midi_data) # Apply transform >>> pretty_midi_obj = ConvertToPrettyMIDI()(transformed) # Convert back if needed
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', tempo_range=(30.0, 200.0), p=0.2, respect_tempo_shifts=True, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the TempoShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum value by which tempo can be randomly shifted (in BPM).
mode (str, optional) – Direction of tempo shift (‘up’, ‘down’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
tempo_range (tuple[float, float], optional) – Allowed tempo range in BPM. Default: (30.0, 200.0)
p (float, optional) – Probability of applying the transform. Default: 0.2
respect_tempo_shifts (bool, optional) – Whether to preserve multiple tempo events. Default: True
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the tempo shift transformation to the MIDI data.
This method handles several cases: 1. Empty MIDI file (returns unchanged) 2. No tempo events (adds default 120 BPM) 3. Single tempo event 4. Multiple tempo events (based on respect_tempo_shifts)
- Parameters:
midi_data (mido.MidiFile) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with modified tempo(s).
- Return type:
mido.MidiFile
Note
If no tempo events are found, a default tempo of 120 BPM is used.
Only tempo events in the first track are processed.
When respect_tempo_shifts is True, all tempo events maintain their relative timing but get new tempo values.
When respect_tempo_shifts is False, all tempo events are replaced with a single tempo event at the start.
The transform is applied with probability self.p. If not applied, the original tempo(s) are preserved.
Module contents
MIDI data augmentation transforms.
This module provides a collection of transforms for augmenting MIDI data. These transforms can be used individually or composed together to create complex augmentation pipelines.
- Available Transforms:
DurationShift: Randomly modify note durations while keeping onset times intact
NoteAdd: Randomly add new notes to instrument tracks
NoteDelete: Randomly remove notes from instrument tracks
OnsetTimeShift: Randomly shift note onset times while preserving durations
PitchShift: Randomly transpose note pitches up or down
TempoShift: Randomly modify tempo while preserving relative note timing
- All transforms follow a consistent interface inherited from BaseMidiTransform:
They are callable objects that take a PrettyMIDI object as input
They support probabilistic application through the ‘p’ parameter
They handle multi-instrument MIDI files through the ‘p_instruments’ parameter
Example
>>> from midiogre.augmentations import PitchShift, OnsetTimeShift
>>> from midiogre.core import Compose
>>> import pretty_midi
>>>
>>> # Create transform pipeline
>>> transform = Compose([
... PitchShift(max_shift=2, p=0.5),
... OnsetTimeShift(max_shift=0.1, p=0.3)
... ])
>>>
>>> # Load and transform MIDI file
>>> midi_data = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI('song.mid')
>>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
See also
midiogre.core.transforms_interface: Base class and interface for all transforms midiogre.core.compositions: Tools for composing multiple transforms
- class midiogre.augmentations.DurationShift(max_shift, mode='both', min_duration=1e-06, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly modifying MIDI note durations.
This transform allows for random modification of note durations while preserving their onset times. Each selected note can be shortened or lengthened by a random amount within the specified range. The shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for varied articulation.
The duration shift is applied with probability p to each selected instrument, and within each instrument, to a random subset of notes determined by p. All shifts are automatically clipped to ensure notes maintain a minimum duration and don’t extend beyond the track end.

- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds by which a note duration can be modified. Must be positive.
mode (str) – Type of duration modification. One of: - ‘shrink’: Only shorten notes - ‘extend’: Only lengthen notes - ‘both’: Allow both shortening and lengthening Default: ‘both’
min_duration (float) – Minimum allowed note duration in seconds. Notes will not be shortened below this value. Default: 1e-6
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the probability of modifying each note. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - max_shift is not positive - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘shrink’, ‘extend’ - min_duration is not positive - p_instruments is not in range [0, 1] - p is not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that only extends notes by 0.1-0.3 seconds >>> transform = DurationShift( ... max_shift=0.3, ... mode='extend', ... min_duration=0.1, ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.4 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', min_duration=1e-06, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the DurationShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds for duration modifications.
mode (str, optional) – Type of duration modification (‘shrink’, ‘extend’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
min_duration (float, optional) – Minimum allowed note duration in seconds. Default: 1e-6
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Probability of modifying each note. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the duration shift transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Randomly selects a subset of notes based on p 2. Generates random duration shifts based on mode and max_shift 3. Applies the shifts while maintaining onset times and ensuring valid durations
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with modified note durations.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The transform maintains the onset time of all notes
Notes are modified independently, allowing for varied articulation
- Duration changes are clipped to ensure:
Notes maintain the minimum duration
Notes don’t extend beyond the end of the track
- class midiogre.augmentations.NoteAdd(note_num_range, note_velocity_range, note_duration_range, restrict_to_instrument_time=True, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly adding new MIDI notes.
This transform allows for random addition of new notes to MIDI tracks. Each new note’s properties (pitch, velocity, duration, timing) are randomly generated within specified ranges. The number of notes added is proportional to the existing number of notes in each track.
The note addition is applied with probability p to each selected instrument. For each selected instrument, the number of notes to add is randomly chosen between 0 and p * (current number of notes).
- Parameters:
note_num_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI note numbers for new notes as (min_note, max_note). Each value must be in range [0, 127]. Example: (60, 72) for notes between middle C and C5.
note_velocity_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI velocities for new notes as (min_velocity, max_velocity). Each value must be in range [0, 127]. Example: (64, 100) for medium to loud notes.
note_duration_range (tuple[float, float]) – Range of note durations in seconds as (min_duration, max_duration). Values must be positive. Example: (0.1, 0.5) for short to medium notes.
restrict_to_instrument_time (bool) – If True, new notes will not extend beyond the end time of existing notes in the instrument. Default: True
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the maximum ratio of new notes to add relative to existing notes. Must be in range [0, 1]. Example: If p=0.2 and an instrument has 100 notes, up to 20 new notes may be added. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - note_num_range values not in [0, 127] - note_velocity_range values not in [0, 127] - note_duration_range values not positive - ranges not specified as (min, max) with max > min - p_instruments not in range [0, 1] - p not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that adds short, quiet notes in the high register >>> transform = NoteAdd( ... note_num_range=(72, 96), # C5 to C7 ... note_velocity_range=(20, 40), # Soft notes ... note_duration_range=(0.05, 0.2), # Short notes ... restrict_to_instrument_time=True, ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.15 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(note_num_range, note_velocity_range, note_duration_range, restrict_to_instrument_time=True, p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the NoteAdd transform.
- Parameters:
note_num_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI note numbers for new notes.
note_velocity_range (tuple[int, int]) – Range of MIDI velocities for new notes.
note_duration_range (tuple[float, float]) – Range of note durations in seconds.
restrict_to_instrument_time (bool, optional) – Whether to limit note end times. Default: True
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Maximum ratio of new notes to add. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the note addition transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Determines the number of notes to add based on p 2. Generates random notes within the configured ranges 3. Adds the new notes to the instrument track
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with added notes.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The number of notes added is random but proportional to existing notes
New notes have random properties within the configured ranges
If restrict_to_instrument_time is True, new notes won’t extend beyond the end of existing notes in the track
- class midiogre.augmentations.NoteDelete(p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly deleting MIDI notes.
This transform allows for random deletion of existing notes from MIDI tracks. The deletion is applied with probability p to each selected instrument. For each selected instrument, the number of notes to delete is randomly chosen between 0 and p * (current number of notes).
- Parameters:
p_instruments (float, optional) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float, optional) – For each selected instrument, this determines the maximum ratio of notes that may be deleted. Must be in range [0, 1]. Example: If p=0.2 and an instrument has 100 notes, up to 20 notes may be deleted. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - p_instruments not in range [0, 1] - p not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that aggressively thins out notes >>> transform = NoteDelete( ... p_instruments=0.8, # Apply to 80% of instruments ... p=0.4, # Delete up to 40% of notes ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the NoteDelete transform.
- Parameters:
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Maximum ratio of notes that may be deleted. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the note deletion transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Determines the number of notes to delete based on p 2. Randomly selects notes for deletion 3. Removes the selected notes from the instrument track
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with notes deleted.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The number of notes deleted is random but proportional to existing notes
Notes are selected for deletion uniformly at random
Empty instruments (no notes) are skipped
- class midiogre.augmentations.OnsetTimeShift(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly shifting MIDI note onset times.
This transform allows for random modification of note start times while preserving their durations. Each selected note can be shifted earlier or later in time by a random amount within the specified range. The shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for complex rhythmic variations.
The onset shift is applied with probability p to each selected instrument, and within each instrument, to a random subset of notes determined by p. All shifts are automatically clipped to ensure notes stay within valid time ranges (no negative start times, no extending beyond track end).
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds by which a note onset can be shifted. Must be positive.
mode (str) – Direction of time shift. One of: - ‘left’: Only shift notes earlier (ie, advance) in time - ‘right’: Only shift notes later (ie, delay) in time - ‘both’: Allow both earlier and later shifts Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the probability of shifting each note. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - max_shift is not positive - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘left’, ‘right’ - p_instruments is not in range [0, 1] - p is not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that only delays notes by 0.05-0.15 seconds >>> transform = OnsetTimeShift( ... max_shift=0.15, ... mode='right', ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.3 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the OnsetTimeShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum time in seconds for onset shifts.
mode (str, optional) – Direction of time shift (‘left’, ‘right’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Probability of shifting each note. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the onset time shift transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Randomly selects a subset of notes based on p 2. Generates random time shifts based on mode and max_shift 3. Applies the shifts while maintaining note durations and ensuring valid times
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with shifted note timings.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The transform maintains the duration of all notes
Notes are shifted independently, allowing for complex rhythmic variations
- Shifts are clipped to ensure notes stay within valid time ranges:
No negative start times
No extending beyond the end of the track
- class midiogre.augmentations.PitchShift(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly transposing MIDI note pitches.
This transform allows for random transposition of MIDI notes while preserving their timing and velocity. Each selected note can be shifted up or down by a random amount within the specified range. The shifts are applied on a per-note basis, allowing for complex harmonic variations.
The pitch shift is applied with probability p to each selected instrument, and within each instrument, to a random subset of notes determined by p. All shifts are automatically clipped to stay within the valid MIDI note range [0, 127].

- Parameters:
max_shift (int) – Maximum number of semitones by which a note pitch can be shifted. Must be in range [0, 127].
mode (str) – Direction of pitch shift. One of: - ‘up’: Only shift pitches up - ‘down’: Only shift pitches down - ‘both’: Allow both up and down shifts Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float) – If a MIDI file has multiple instruments, this determines the probability of applying the transform to each instrument. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 1.0 (apply to all instruments)
p (float) – For each selected instrument, this determines the probability of shifting each note. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - max_shift is not in range [0, 127] - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘up’, ‘down’ - p_instruments is not in range [0, 1] - p is not in range [0, 1]
Example
>>> # Create transform that only shifts pitches up by 1-3 semitones >>> transform = PitchShift( ... max_shift=3, ... mode='up', ... p_instruments=1.0, ... p=0.5 ... ) >>> transformed = transform(midi_data)
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', p_instruments=1.0, p=0.2, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the PitchShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (int) – Maximum number of semitones for pitch shifts.
mode (str, optional) – Direction of pitch shift (‘up’, ‘down’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
p_instruments (float, optional) – Probability of applying to each instrument. Default: 1.0
p (float, optional) – Probability of shifting each note. Default: 0.2
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the pitch shift transformation to the MIDI data.
For each non-drum instrument selected based on p_instruments, this method: 1. Randomly selects a subset of notes based on p 2. Generates random pitch shifts based on mode and max_shift 3. Applies the shifts while clipping to valid MIDI note range [0, 127]
- Parameters:
midi_data (pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with shifted pitches.
- Return type:
pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI
Note
Drum instruments are skipped by default
The transform maintains the original timing and velocity of all notes
Notes are shifted independently, allowing for complex harmonic variations
- class midiogre.augmentations.TempoShift(max_shift, mode='both', tempo_range=(30.0, 200.0), p=0.2, respect_tempo_shifts=True, eps=1e-12)[source]
Bases:
BaseMidiTransformTransform for randomly modifying MIDI tempo.
This transform allows for random modification of MIDI tempo while preserving the relative timing of notes. It can either respect all existing tempo changes in the file or replace them with a single global tempo.
Note
This transform operates on Mido MidiFile objects. If you have a PrettyMIDI object, you must first convert it using MIDIOgre’s converters: >>> from midiogre.core.conversions import ConvertToMido >>> midi_data = ConvertToMido()(pretty_midi_obj)
The tempo shift is applied with probability p, and when applied, generates random shifts based on the specified mode and maximum shift value. The final tempo is always clipped to stay within the specified tempo range.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum value by which tempo can be randomly shifted (in BPM). Must be positive.
mode (str) – Direction of tempo shift. One of: - ‘up’: Only increase tempo - ‘down’: Only decrease tempo - ‘both’: Allow both increase and decrease Default: ‘both’
tempo_range (tuple[float, float]) – Allowed tempo range in BPM as (min_tempo, max_tempo). The transformed tempo will be clipped to stay within this range. Default: (30.0, 200.0)
p (float) – Probability of applying the tempo shift. Must be in range [0, 1]. Default: 0.2
respect_tempo_shifts (bool) – If True, preserves all tempo change events, shifting each while maintaining their timing. If False, replaces all tempo events with a single tempo at the start. Default: True
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If any of the following conditions are met: - mode is not one of ‘both’, ‘up’, ‘down’ - max_shift is not positive - tempo_range is not a tuple/list of length 2 - min_tempo is negative - min_tempo >= max_tempo
Example
>>> from midiogre.core.conversions import ConvertToMido, ConvertToPrettyMIDI >>> # Create transform that increases tempo by 10-30 BPM >>> transform = TempoShift( ... max_shift=30.0, ... mode='up', ... tempo_range=(60.0, 240.0), ... p=1.0 ... ) >>> midi_data = ConvertToMido()('song.mid') # Convert to Mido format >>> transformed = transform(midi_data) # Apply transform >>> pretty_midi_obj = ConvertToPrettyMIDI()(transformed) # Convert back if needed
- __init__(max_shift, mode='both', tempo_range=(30.0, 200.0), p=0.2, respect_tempo_shifts=True, eps=1e-12)[source]
Initialize the TempoShift transform.
- Parameters:
max_shift (float) – Maximum value by which tempo can be randomly shifted (in BPM).
mode (str, optional) – Direction of tempo shift (‘up’, ‘down’, or ‘both’). Default: ‘both’
tempo_range (tuple[float, float], optional) – Allowed tempo range in BPM. Default: (30.0, 200.0)
p (float, optional) – Probability of applying the transform. Default: 0.2
respect_tempo_shifts (bool, optional) – Whether to preserve multiple tempo events. Default: True
eps (float, optional) – Small epsilon value for numerical stability. Default: 1e-12
- Raises:
ValueError – If parameters are invalid (see class docstring for details).
- apply(midi_data)[source]
Apply the tempo shift transformation to the MIDI data.
This method handles several cases: 1. Empty MIDI file (returns unchanged) 2. No tempo events (adds default 120 BPM) 3. Single tempo event 4. Multiple tempo events (based on respect_tempo_shifts)
- Parameters:
midi_data (mido.MidiFile) – The MIDI data to transform.
- Returns:
The transformed MIDI data with modified tempo(s).
- Return type:
mido.MidiFile
Note
If no tempo events are found, a default tempo of 120 BPM is used.
Only tempo events in the first track are processed.
When respect_tempo_shifts is True, all tempo events maintain their relative timing but get new tempo values.
When respect_tempo_shifts is False, all tempo events are replaced with a single tempo event at the start.
The transform is applied with probability self.p. If not applied, the original tempo(s) are preserved.